Exam 5 (covering Module 8 – Network Security) is posted in Canvas. Due on Thursday, April 30th, by 11.59 PM for both graduating and non-graduating students.
—————————————————–
Socket Programming Code and Videos
Sample Classroom Lecture Videos
Dr. Meg's Desktop Selected Lecture Videos
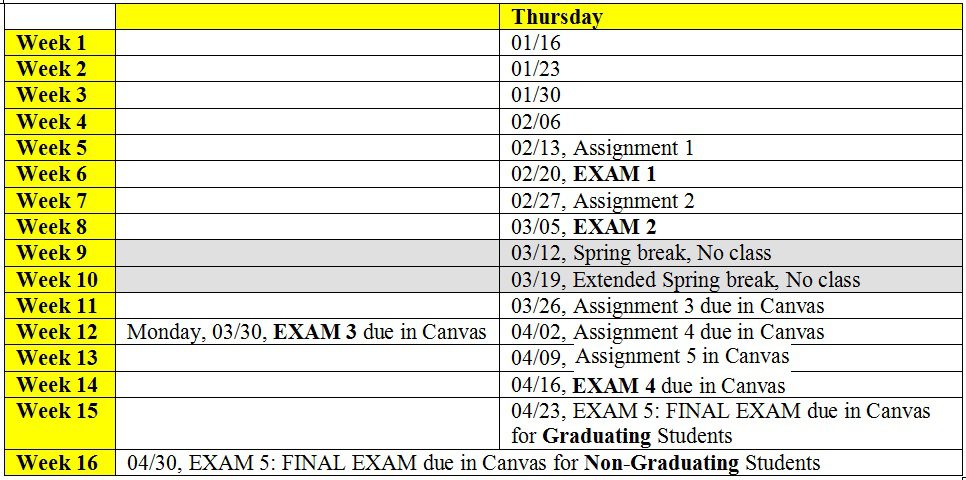
Quiz, Exam and Project Schedules
—————————————————–
Syllabus
CSC 435/524 Syllabus, Spring 2020
Lecture Slides
Module 1: IP/MAC Addresses and TCP/IP Suite
Module 2: Socket Programming in Java
Module 4: LANs and Extended LANs
Question Bank
Question Bank for Module 1: IP/MAC Addresses: TCP/IP Suite
Question Bank for Module 2: Socket Programming in Java
Question Bank for Module 3: Physical Layer
Question Bank for Module 4: Local Area Networks
Question Bank for Module 5: Routing Protocols
Question Bank for Module 6: Internet Layer
Question Bank for Module 7: Transport Layer
Question Bank for Module 8: Network Security
Assignments
Assignment 3: Simulation using Cisco Packet Tracer Configuration of VLANs across Multiple Broadcast Domains. Due on March 26th, by 11.59 PM.
Assignment 4: Undergraduate Version (Cisco Packet Tracer: Wireless Router Configuration). Due on April 2nd, by 11.59 PM. See the Assignments section.
Assignment 4: Graduate Version (Cisco Packet Tracer: Wireless Router Configuration). Due on April 2nd, by 11.59 PM. See the Assignments section.
Exams
Exam 3 (Take Home): Due in Canvas on Monday, March 30th, by 11.59 PM
Exam 4 (Take Home): Due in Canvas on Friday, April 17th, by 11.59 PM
Socket Programming Code and Videos
| Topics | Desktop Recorded Videos | Java Code of the Socket Programs (zipped) | In-Class Lecture Videos |
| Module 2 – Socket Programming (Datagram Connectionless Sockets) | Intro Ex 3.1 Ex 3.2 | Ex 3.1 Ex 3.2 | Part a Part b Part c |
| Module 2 – Socket Programming (Connection-Oriented Sockets) | Ex 4.1 Ex 4.2 Ex 4.3 Ex 4.4 Ex 4.5 | Ex 4.1 Ex 4.2 Ex 4.3 Ex 4.4 Ex 4.5 | Part a Part b Part c |
| Module 2 – Socket Programming (Iterative vs. Concurrent Server; Thread Programming) | Ex 4.6.1 Ex 4.6.2 | Ex 4.6.1 Ex 4.6.2 | Part a Part b |
| Module 2 – Socket Programming (Multicast Sockets) | Ex 5.1 Ex 5.2 | Ex 5.1 Ex 5.2 | Part a Part b Part c |
Sample Classroom Lecture Videos
| Date | Topics | Videos |
| Aug 28, 2013 |
Module 2 – Socket Programming (Datagram Connectionless Sockets); Module 1 – IP Addressing (Class-based Addressing; Private IP Address; Examples) |
Module 2: Part a Part b Part c Module 1: Part d Part e Part f Part g |
| Sep 4, 2013 |
Module 2 – Socket Programming (Connection-Oriented Sockets); Module 1 – IP Addressing (Subnetting – Examples) |
Module 2: Part a Part b Part c Module 1: Part d Part e Part f Part g |
| Sep 9, 2013 |
Module 2 – Socket Programming (Iterative vs. Concurrent Server; Thread Programming); Module 1 – IP Addressing (Subnetting and CIDR – Examples) |
Module 2: Part a Part b Module 1: Part c Part d Part e Part f Part g |
| Sep 11, 2013 |
Module 2 – Socket Programming (Multicast Sockets); Module 1 – Packet Transmission in the Internet and TCP/IP Protocol Suite; Module 3 – Physical Layer (3.1: Baud rate and Bit rate) |
Module 2: Part a Part b Part c Module 1: Part d Part e Part f Module 3: Part g Part h |
| Sep 16, 2013 | Module 3 – Physical Layer (3.1: Baud rate and Bit rate; 3.2: Channel Encoding Standards; 3.3: Transmission Order of Bytes; 3.4: Amplitude Modulation) | Part a Part b Part c Part d |
| Sep 18, 2013 | Module 3 – Physical Layer (3.4: Frequency and Phase Modulation; 3.5: Multiplexing Techniques) | Part a Part b Part c Part d Part e |
| Oct. 2, 2013 | Module 4: 4.1 – LANs | Part a Part b Part c Part d Part e |
| Oct. 7, 2013 | Module 4: 4.2 – Extended LANs and Networking Devices | Part a Part b Part c Part d Part e |
| Oct. 9, 2013 |
Module 4: 4.3 – VLANs and Ethernet Cables Module 5: 5.1 – Principles of Routing in the Internet and 5.2 – Distance Vector Routing Examples |
Part a Part b Part c Part d Part e |
| Oct. 14, 2013 | Module 5: 5.2 Distance Vector Routing – Count-to-Infinity Problem; 5.3 Link State Routing; 5.4 Inter Domain Routing; 5.5 Multicast Routing – Efficiency Calculations | Part a Part b Part c Part d Part e Part f |
| Oct. 16, 2013 | Module 5: 5.5 Multicast Routing Protocols | Part a Part b Part c |
| Oct. 21, 2013 | Module 6: 6.1 IP Header (v4) and 6.2: IP Fragmentation | Part a Part b Part c Part d Part e |
| Oct. 23, 2013 |
Module 6: 6.2: IP Fragmentation (Examples and Math Problem) 6.3: IP Datagram Forwarding (Examples) |
Part a Part b Part c Part d Part e Part f |
| Oct. 28, 2013 | Module 6: 6.2: IP Fragmentation and 6.4 Ping Command | Part a: MTU Discovery using Ping Command and Binary Search |
| Oct. 28, 2013 | Module 6: 6.3: IP Datagram Forwarding and 6.4: Auxiliary Protocols | Part b Part c Part d Part e Part f Part g |
| Nov. 4, 2013 |
Module 6: 6.5: IPv6 Module 7: Transport Layer – 7.1: UDP vs. TCP; 7.2: UDP Header; 7.3: TCP Header |
Part a Part b Part c Part d Part e |
| Nov. 6, 2013 | Module 7: Transport Layer – 7.3: TCP Header and Connection Establishment; 7.4 – Flow Control | Part a Part b Part c |
| Nov. 11, 2013 | Module 7: Transport Layer – 7.3: TCP Header and Connection Establishment; 7.4 – Retransmission Timeout Algorithm and Congestion Control | Part a Part b Part c |
| Nov. 13, 2013 | Module 7: Transport Layer – 7.4 – Congestion Control Algorithms, Advertised Window Size and Sequence Number Space | Part a Part b Part c Part c |
| Nov. 13, 2013 |
Module 7: Transport Layer: 7.4: Relationship between Advertised Window Size and Sequence Number Space |
Part 1: Theory: Relation, RTT*Bandwidth, MSL*Bandwidth
|
| Nov. 18, 2013 | Module 7: Transport Layer – 7.4 – Math Problems on TCP: Advertised Window, Sequence Number Space, Congestion Control, Throughput, etc | Part a Part b Part c Part c Part c |
Dr. Meg's Desktop Selected Lecture Videos (YouTube Links)
Video to Show How to Setup Java Path in Windows 7
Module 1: IP Address/MAC Address and TCP/IP Suite
CIDR: Classless Interdomain Routing with Example
Module 2: Java Socket Programming
Datagram Sockets (Connectionless Sockets): Sender Receiver Unicast (Example 3.1)
Datagram Sockets (Connectionless Sockets): Duplex Sender Receiver (Example 3.2)
Stream Sockets (Connection-Oriented Sockets): Client Server (Example 4.1)
Stream Sockets (Connection-Oriented Sockets): Duplex Client Server (Example 4.2)
Stream Sockets (Connection-Oriented Sockets): Infinite Loop Server (Example 4.3)
Stream Sockets (Connection-Oriented Sockets): Sending Objects (Example 4.4)
Stream Sockets (Connection-Oriented Sockets): Sending Integer (Example 4.5)
Stream Sockets (Connection-Oriented Sockets): Summation Server – Iterative (Example 4.6.1)
Stream Sockets (Connection-Oriented Sockets): Summation Server – Concurrent (Example 4.6.2)
Multicast Sockets: One Sender Multiple Receivers (Example 5.1)
Multicast Sockets: Multicast Sender Receiver (Example 5.2)